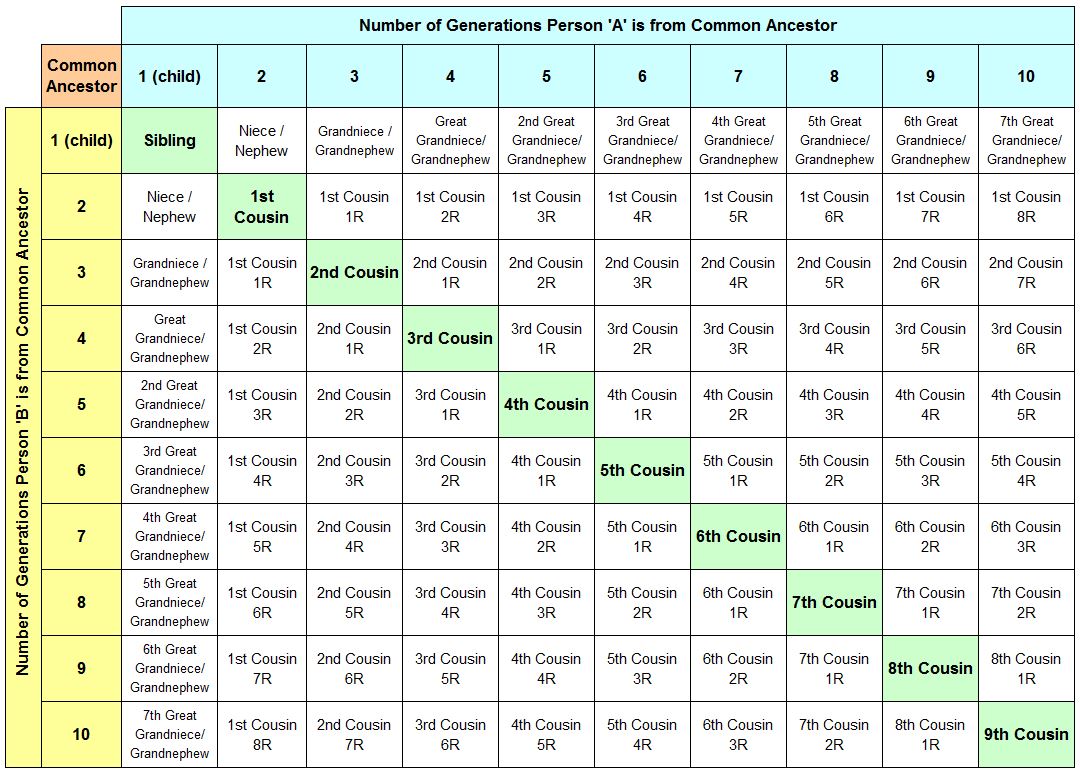
Example-1: If two people are the SAME number of generations away from the common ancestors, they are '# cousins', where;
'#' is ONE LESS than the number of generations. So, if two people are both 4 generations from the common ancestor, they are "3rd cousins".
Example-2: If two people are DIFFERENT numbers of generations away from the common ancestors, they are '# cousins X removed,
where;
'#' is ONE LESS than the LESSOR of the two differences of generations from the common ancestor, and
'X' is the difference between the number of generations.
So, if one person is 3 generations from the common ancestor and the other person is 5 generations away, they are "2nd cousins twice removed".
They are 2nd cousins, because 3 is less than 5, so 3 - 1 = 2.
They are twice removed (2R), because the difference between 3 and 5 is 2.
Summary: Based on the two example, relationships can be calculated between any two people, regardless of the number of generations they are from the common ancestor.